Stargate Interface
Technology from Stargate Journey (mainly Stargates) can be controlled with computers from ComputerCraft. This is achieved through the use of Interfaces, which, as the name suggests, interface with alien technology and enable you to control it.
They can read information from a Stargate and provide a redstone signal with a comparator. And they can also act as computercraft peripherals.
There are three available Stargate Interfaces - Basic Interface, Crystal Interface, Advanced Crystal Interface.
Unless there is a label with interface name at the function, it can be used by any interface.
If there is a label, the function is only available for the specified interface.A similar applies to return values. Some return values might only be available for crystal or advanced crystal interface.
Crystal Interface Advanced Crystal Interface
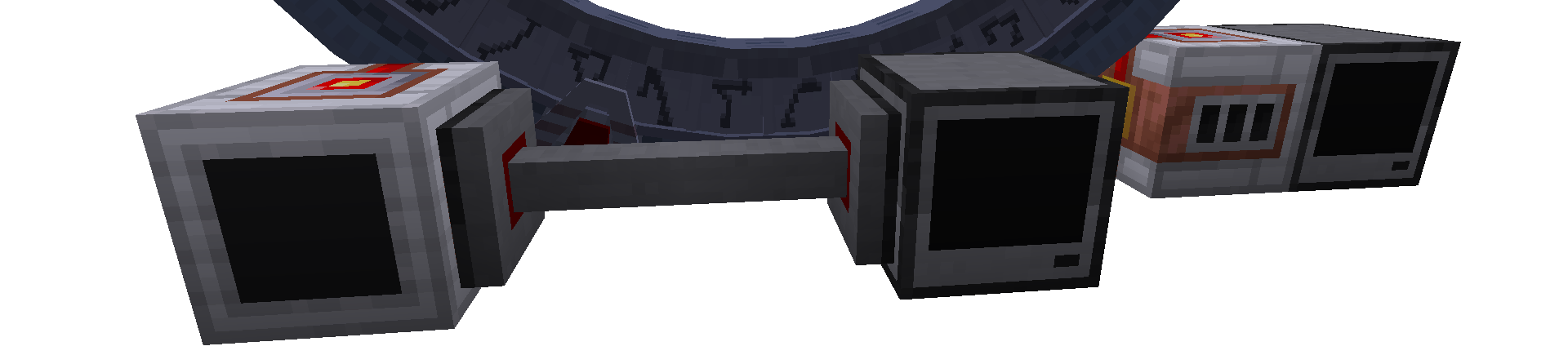
Connecting the interface
The interface needs to face the stargate (the blank black side must face away from the gate).
The computer needs to be either placed right next to the interface, the side does not matter. Or you need to connect the interface using a cable modem. Note that the cable modems on both sides need to be activated by right-clicking, lighting them red.

In the program, interface can be acquired using the find function.
local interface = peripheral.find("basic_interface")
if interface == nil then
printError("The interface is not connected")
return
end
You can also instruct the program to use any available interface type, but keep in mind that not all features are available for all interface types.
local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface")
if interface == nil then
error("The interface is not connected")
end
Functions
Common functions
These are the functions every Interface has available at all times.
addressToString
(address)
source Converts the array specified by address to a form used elsewhere in the mod (-1-2-3-4-5-6-).
Parameters
address:number[]The array of numbers representing an address.
Returns
stringThe address in text form used elsewhere in the mod. Returns"-"when the address is empty or has more than 8 symbols.
Usage
- Convert the abydos address to text
-26-6-14-31-11-29--- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local stringAddress = interface.addressToString({ 26, 6, 14, 31, 11, 29 }) print(stringAddress) -- prints -26-6-14-31-11-29-
Lua equivalent
function addressToString(address)
if #address == 0 or #address > 8 then
return "-"
end
return "-" .. table.concat(address, "-") .. "-"
end
getEnergy
()
source Returns the current amount of energy [FE (Forge Energy)] stored in the interface.
Returns
numberThe energy [FE] stored within the interface
See also
Usage
- Print the current amount of energy in the interface
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local energy = interface.getEnergy() print("There is "..energy.." FE in the interface")
getEnergyCapacity
()
source Returns the maximal amount of energy [FE] that can be stored in the interface.
Returns
numberThe interface capacity
Usage
- Print the energy capacity of the interface
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local capacity = interface.getEnergyCapacity() print("The interface can store up to "..capacity.." FE")
getEnergyTarget
()
source Returns the current energy target that is set for the interface.
Returns
numberThe current energy target [FE]
See also
Usage
- Print the current energy target
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local energyTarget = interface.getEnergyTarget() print("The current energy target: "..energyTarget.." FE")
setEnergyTarget
(energyTarget)
source Sets the energy target to the amount specified by energyTarget parameter.
Parameters
energyTarget:numberThe new energy target
See also
Usage
- Set a new energy target
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: -- the amount of energy [FE] required to reach another galaxy by default (100 000 000 000) local energyTarget = 100000000000 interface.setEnergyTarget(energyTarget)
Milky Way Stargate functions
Functions available for an interface connected to the Milky Way Stargate.
closeChevron
()
source Closes the upper chevron if it is open, encoding the current symbol.
If the symbol is already encoded, returns -2 (symbol_in_address).
Returns
numberThe recent Stargate Feedback[int]stringCrystal InterfaceAdvanced Crystal InterfaceA description of the feedback
See also
Usage
- Close chevron
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local feedback = interface.closeChevron() print(feedback)
encodeChevron
()
source Encodes the current symbol under the top chevron. Requires the chevron to be open, otherwise returns -35 (chevron_not_raised).
Returns
numberThe recent Stargate Feedback[int]stringCrystal InterfaceAdvanced Crystal InterfaceA description of the feedback
See also
Usage
- Encode chevron
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local feedback = interface.encodeChevron() print(feedback)
endRotation
()
source Stops the inner ring rotation if it was started by a computer.
Does nothing if the ring rotates due to a redstone signal.
Returns
numberThe recent Stargate Feedback[int]stringCrystal InterfaceAdvanced Crystal InterfaceA description of the feedback
See also
Usage
- End the ring rotation
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local feedback = interface.endRotation() print(feedback)
getCurrentSymbol
()
source Returns the current symbol under the top chevron.
Returns
numberThe symbol under the top chevron
Usage
- Print the current symbol
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local symbol = interface.getCurrentSymbol() print(symbol)
getRotation
()
source Returns the current inner ring rotation from 0 up to 155 (inclusive).
0when the Point of Origin is centered under the top chevron
plus4for each symbol to the right centered under the top chevron
152for the last symbol (38) centered under the top chevron.
Returns
numberThe current ring rotation from0to155
See also
Usage
- Check current ring rotation
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: while true do local rotation = interface.getRotation() print(rotation) sleep(0) end
isChevronOpen
()
source Returns true when the top chevron is open, false otherwise.
Returns
booleanWhether the top chevron is open
See also
Usage
- Check whether the top chevron is open
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local isOpen = interface.isChevronOpen() if isOpen then print("The chevron is open") else print("The chevron is closed") end
isCurrentSymbol
(symbol)
source Returns true when the current symbol is centered under the top chevron, and it is the desired symbol specified as parameter. Returns false otherwise.
Parameters
symbol:numberThe desired symbol
Returns
booleanWhether the current symbol is centered under the top chevron and matches the desired symbol.
See also
Usage
- Await the rotation completion
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local symbol = 15 interface.rotateClockwise(symbol) while not interface.isCurrentSymbol(symbol) do sleep(0) end -- rotation complete print("The current symbol is "..symbol)
openChevron
()
source Opens the top chevron in preparation for encoding the current symbol.
Returns
numberThe recent Stargate Feedback[int]stringCrystal InterfaceAdvanced Crystal InterfaceA description of the feedback
See also
Usage
- Open the top chevron
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local feedback interface.openChevron() print(feedback)
rotateAntiClockwise
(symbol)
source Rotates the inner ring anticlockwise, positioning the specified symbol centered under the top chevron.
The method does not block the execution for the whole rotation.
The rotation is stopped when the interface is destroyed.
Parameters
symbol:numberThe desired symbol (from0to38inclusive), or-1for infinite rotation.
Returns
numberThe recent Stargate Feedback[int]stringCrystal InterfaceAdvanced Crystal InterfaceA description of the feedback
Throws
- When the chevron is open or the symbol is out of range (lower than
-1or higher than38).
See also
Usage
- Rotate the ring anticlockwise to the symbol
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local symbol = 15 -- start the rotation interface.rotateAntiClockwise(symbol) -- await the completion while not interface.isCurrentSymbol(symbol) do sleep(0) end -- rotation complete print("The current symbol is "..symbol)
rotateClockwise
(symbol)
source Rotates the inner ring clockwise, positioning the specified symbol centered under the top chevron.
The method does not block the execution for the whole rotation.
The rotation is stopped when the interface is destroyed.
Parameters
symbol:numberThe desired symbol (from0to38inclusive), or-1for infinite rotation
Returns
numberThe recent Stargate Feedback[int]stringCrystal InterfaceAdvanced Crystal InterfaceA description of the feedback
Throws
- When the chevron is open or the symbol is out of range (lower than
-1or higher than38).
See also
Usage
- Rotate the ring clockwise to the symbol
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local symbol = 15 -- start the rotation interface.rotateClockwise(symbol) -- await the completion while not interface.isCurrentSymbol(symbol) do sleep(0) end -- rotation complete print("The current symbol is "..symbol)
Stargate functions
Functions available for an interface connected to a Stargate.
disconnectStargate
()
source Disconnects the Stargate if there is an active connection. The Stargate will be reset if it isn’t connected (encoded chevrons will be deactivated).
The Stargate won’t disconnect/reset if the connection is currently forming (before the kawoosh finishes).
Returns
booleantrueif the connection was closed,falseif there was no connection or the Stargate failed to disconnect (e.g. function was called during kawoosh).
Usage
- Disconnect the Stargate
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local result = interface.disconnectStargate() if result then print("Stargate disconnected") else print("Stargate is not open / Can not disconnect") end
getChevronsEngaged
()
source Returns a number from 0 to 9 which represents a number of chevrons that are engaged on the Stargate.
Returns
numberThe number of chevrons that have been engaged (0 - 9).
Usage
- Print the number of engaged chevrons
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local engaged = interface.getChevronsEngaged() print("Stargate has "..engaged.."/9 chevrons engaged")
getOpenTime
()
source Returns a number of ticks for which Stargate has been active.
Returns
numberThe number of ticks the Stargate has been active for, returns0if it’s inactive.
See also
Usage
- Print a number of seconds for which the Stargate has been active
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local openTimeInTicks = interface.getOpenTime() -- each second has 20 ticks local openTimeInSeconds = math.floor(openTimeInTicks / 20) print("Stargate has been open for "..openTimeInSeconds.." seconds")
getRecentFeedback
()
source Returns information about the Stargate state.
For Advanced Crystal interface also returns a second string value with a status description.
Returns
numberThe most recent Stargate Feedback[int]stringCrystal InterfaceAdvanced Crystal InterfaceA description of the feedback
See also
- Because the wiki can quickly become outdated,
you can check the feedback codes in the mod source code.
Usage
- Print the recent feedback
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local feedbackCode, feedbackMessage = interface.getRecentFeedback() print("Feedback code: "..feedbackCode) if feedbackMessage then print(feedbackMessage) else print("No description - advanced crystal interface required") end
getStargateEnergy
()
source Returns the amount of energy currently stored in the Stargate.
Returns
numberThe energy [FE] stored within the Stargate
See also
Usage
- Print the current amount of energy in the Stargate
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local energy = interface.getEnergy() print("There is "..energy.." FE in the Stargate")
getStargateGeneration
()
source Returns the Stargate generation identifier.
0- Classic Stargate
1- Universe Stargate
2- Milky Way Stargate, Tollan Stargate
3- Pegasus
Returns
numberThe generation[int]of the Stargate
See also
Usage
- Print the Stargate generation
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local generation = interface.getStargateGeneration() print("The Stargate is "..generation.." generation")
getStargateType
()
source Returns the minecraft resource identifier for the Stargate.
sgjourney:classic_stargate
sgjourney:universe_stargate
sgjourney:milky_way_stargate
sgjourney:tollan_stargate
sgjourney:pegasus_stargate
Returns
stringThe resource identifier of the Stargate
See also
Usage
- Print the Stargate type
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local type = interface.getStargateType() print("The stargate identifier: "..type)
getStargateVariant
()
source Returns the minecraft resource identifier for the Stargate variant.
Returns
stringThe Stargate variant resource identifier (e.g.sgjourney:milky_way_movie)
orsgjourney:emptyfor the default Stargate variant
See also
Usage
- Print the Stargate variant
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local variant = interface.getStargateVariant() print("The stargate variant: "..variant)
isStargateConnected
()
source Check whether the Stargate is connected to another gate.
The function returns true even before kawoosh.
The Stargate is connected when it establishes a connection.
Once the Point of Origin is successfully encoded or the first chevron is being locked for an incoming connection.
Returns
booleanWhether the Stargate has an active connection
See also
Usage
- Check whether the Stargate is connected
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local isConnected = interface.isStargateConnected() if isConnected then print("Stargate is connected") else print("Stargate is not connected") end
isStargateDialingOut
()
source Returns true when there is an active outgoing connection (this Stargate dialed the other gate).
Returns
booleanWhether the Stargate is currently connected and the connection is outgoing. Returnsfalseotherwise (the Stargate is not connected or the connection is incoming).
See also
Usage
- Check whether the active connection is outgoing
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local isDialingOut = interface.isStargateDialingOut() if isDialingOut then print("Stargate is dialing out") else print("The connection is incoming, or the gate is not active") end
isWormholeOpen
()
source Returns true if there is an active wormhole. After the kawoosh finishes, and it is safe to enter the wormhole, false otherwise.
Returns
booleanWhether the wormhole has formed
See also
Usage
- Check whether the wormhole has formed
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local isOpen = interface.isWormholeOpen() if isOpen then print("Wormhole is open") else print("Wormhole is not open") end - Check whether the wormhole is active and it is safe to enter
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: -- assuming the config uses default values (the reverse wormhole kills) local isConnected = interface.isStargateConnected() local isOpen = interface.isWormholeOpen() local isOutgoing = interface.isStargateDialingOut() if not isConnected then print("The Stargate is not connected") elseif not isOpen then -- The Stargate is connected, but the wormhole has not yet formed. print("The wormhole is forming") elseif isOutgoing then print("The wormhole is safe to enter") else print("The connection is incoming, do not enter the wormhole!") end
sendStargateMessage
(message)
source Sends the message through the current Stargate connection, which can be received by a computer on the other side as event stargate_message_received.
Basic and Crystal interfaces can only send messages after the wormhole has fully formed
(isWormholeOpen returns true).
The Advanced Crystal interface can send a message once the Stargate is connected
(isStargateConnected returns true). Any interface can receive the message.
Parameters
message:stringThe message to send
Returns
booleanWhether the message was sent successfully
See also
Usage
- Send a message
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local message = "Hello from the other side" local wasSent = interface.sendStargateMessage(message) if wasSent then print("Message sent successfully") else print("The message could not be sent") end - Receive a message from the stargate
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local message = os.pullEvent("stargate_message_received") print("Received a message from the Stargate:") print(message)
engageSymbol
(symbol)
source Crystal Interface
Advanced Crystal Interface
Directly encodes the symbol. This method can encode symbols on any Stargate.
Using this method matches dialing with DHD.
For example, the Milky Way Stargate does not need to spin the ring; it just encodes chevrons directly.
Parameters
symbol:numberA symbol to encode. The symbol must be in a supported range by the Stargate type.
Returns
numberThe recent Stargate Feedback[int]stringCrystal InterfaceAdvanced Crystal InterfaceA description of the feedback
See also
Usage
- Dial the address
-- find crystal or advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local address = { 26, 6, 14, 31, 11, 29, 0 } -- Abydos -- don't forgot the zero (Point of Origin) at the end! for _, symbol in pairs(address) do interface.engageSymbol(symbol) sleep(1) end
getDialedAddress
()
source Crystal Interface
Advanced Crystal Interface
Returns the address dialed by the gate.
If the currently active connection is incoming or there is no active connection, the address will be empty.
Returns
number[]: The dialed address
See also
Usage
- Print the dialed address
-- find crystal or advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local address = interface.getDialedAddress() print("The dialed address: " .. interface.addressToString(address))
setChevronConfiguration
(configuration)
source Crystal Interface
Advanced Crystal Interface
Causes the chevrons to encode in the order specified by configuration. This configuration resets every time a Stargate is reset.
Parameters
configuration:number[]An array of length 8 representing the order of chevrons.
Possible chevron numbers are1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8. The top chevron is always encoded as the last one, this can’t be changed.
Chevron numbers
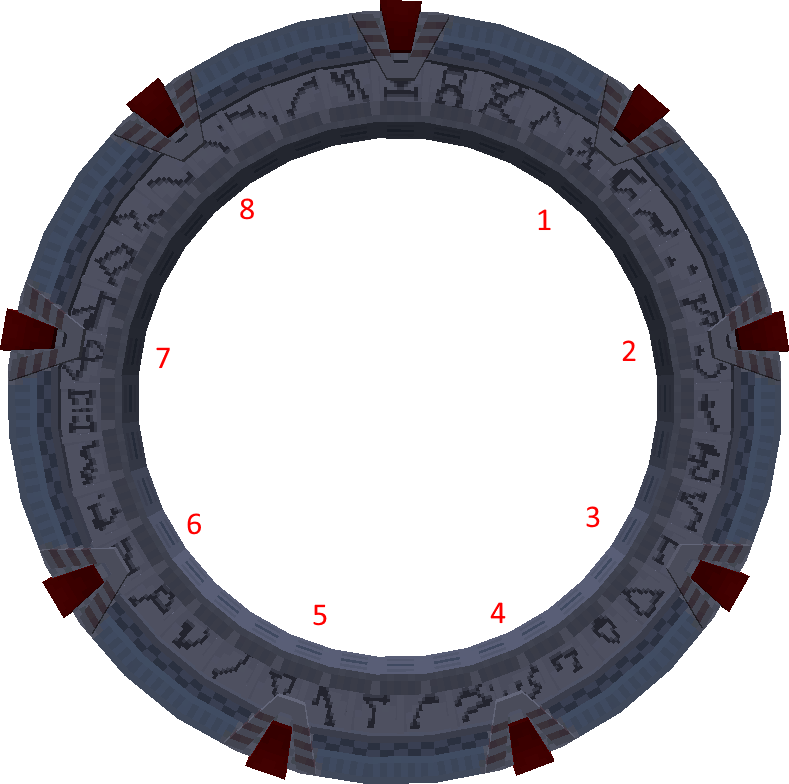
Returns
stringThe message"Chevron configuration set successfully"
Throws
- When specified configuration is invalid. The configuration must be an array of exact length 8 with numbers from 1 to 8 without duplicates.
See also
- disconnectStargate() Resets the Stargate
Usage
- Set the default chevron order
-- find crystal or advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: interface.setChevronConfiguration({1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 4, 5}) - Set clockwise chevron order (e.g. when encoding 9-chevron address).
-- find crystal or advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: interface.setChevronConfiguration({1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8})
addToBlacklist
(address)
source Advanced Crystal Interface
Adds the address to the blacklist. When the filter is set to the blacklist type, the Stargate will not be able to form a connection with the address on the blacklist. That being said, the Stargate can’t dial the address or accept a connection from the blacklisted address.
Blacklisting a 9-chevron address will block all 9-chevron address connections from/to that specific Stargate. However, a connection using a 7/8-chevron address could still be made from/to the Stargate with a blacklisted 9-chevron address. Similarly, blacklisting a 7/8-chevron address will block all 7/8-chevron connections from/to the Stargate. However, it will not block 9-chevron connections from/to such Stargates.
Parameters
address:number[]The 7, 8 or 9-chevron address to be added to the blacklist (without the trailing zero - Point of Origin).
Returns
stringA message describing the result of the action
"Address blacklisted successfully"or"Address is already blacklisted"source
Throws
- When the specified address is invalid (the only allowed lengths are 6, 7 and 8).
See also
Usage
- Blacklist a 9-chevron address
-- find an advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local address = { 16, 25, 4, 21, 6, 19, 33, 22 } interface.clearBlacklist() interface.setFilterType(-1) -- set filter to blacklist mode interface.addToBlacklist(address) -- now the Stargate will not be able to dial the specified address -- or accept a 9-chevron connection from the other gate.
addToWhitelist
(address)
source Advanced Crystal Interface
Adds the address to the whitelist. When the filter is set to the whitelist type, the Stargate will not be able to form a connection with the address that is not on the whitelist. That being said, the Stargate can’t dial the address or accept a connection from an address that is not on the whitelist.
Whitelisting a 9-chevron address will allow all 9-chevron address connections from/to that specific Stargate. However, connections using a 7/8-chevron address would not be possible from/to the Stargate with a whitelisted 9-chevron address unless those addresses are also specifically whitelisted.
Parameters
address:number[]The 7, 8 or 9-chevron address to be added to the whitelist.
Returns
string: A message describing the result of the action
"Address whitelisted successfully"or"Address is already whitelisted"source
Throws
- When the specified address is invalid (the only allowed lengths are 6, 7 and 8).
See also
Usage
- Whitelist the Abydos 7-chevron address
-- find an advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local address = { 26, 6, 14, 31, 11, 29 } interface.clearWhitelist() interface.setFilterType(1) -- set filter to whitelist mode interface.addToWhitelist(address) -- now the Stargate can only estabilish a connection with a Stargate -- on Abydos using the 7-chevron address
clearBlacklist
()
source Advanced Crystal Interface
Removes all addresses from the blacklist.
Returns
string: A message"Blacklist cleared"source
See also
Usage
- Remove all addresses from the blacklist
-- find an advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: interface.clearBlacklist() -- blacklist is now empty
clearWhitelist
()
source Advanced Crystal Interface
Removes all addresses from the whitelist.
Returns
string: A message"Whitelist cleared"source.
See also
Usage
- Remove all addresses from the whitelist
-- find an advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: interface.clearWhitelist() -- whitelist is now empty
getConnectedAddress
()
source Advanced Crystal Interface
Returns the address to which the Stargate is connected (the address on the other side of the connection).
Returns
number[]: The remote 7, 8 or 9-chevron address of the connection
The address is partially filled when a connection is forming and the Stargate is locking the chevrons for an incoming connection.
To ensure the address has full length, the
isWormholeOpen()must return true.For an outgoing connection, the address is always either empty or full-length.
See also
Usage
- Print the remote address
-- find an advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: if interface.isWormholeOpen() then local address = interface.getConnectedAddress() print("The remote address is "..interface.addressToString(address)) else print("Wormhole not formed") end
getFilterType
()
source Advanced Crystal Interface
Returns the numeric identifier of the filter type.
0 None
1 Whitelist
-1 Blacklist
Returns
number: The filter type identifier
See also
Usage
- Print the current filter type
-- find an advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local type = interface.getFilterType() if type == 0 then print("Filter is disabled") elif type == 1 then print("Filter is in whitelist mode") elif type == -1 then print("Filter is in blacklist mode") end
getLocalAddress
()
source Advanced Crystal Interface
Returns the 9-chevron address of this stargate.
Returns
number[]: The address
See also
Usage
- Print the local address
-- find an advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local localAddress = interface.getLocalAddress() print(interface.addressToString(localAddress))
getNetwork
()
source Advanced Crystal Interface
Returns the numeric identifier of the Stargate network of which the Stargate is a part.
Returns
number: The network ID
Default network IDs
0 Classic Stargate
1 Universe Stargate
2 Milky Way Stargate and Tollan Stargate
3 Pegasus Stargate
See also
Usage
- Print the network ID
-- find an advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local network = interface.getNetwork() print("The network ID is: "..network)
isNetworkRestricted
()
source Advanced Crystal Interface
Checks for the network restriction of the Stargate.
Returns
boolean: Whether the Stargate is network restricted
See also
Usage
- Print whether the Stargate is network restricted
-- find an advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local isRestricted = interface.isNetworkRestricted() if isRestricted then print("Network restriction is active") else print("Network restriction is not active") end
removeFromBlacklist
(address)
source Advanced Crystal Interface
Removes the specified address from the blacklist.
Parameters
address:number[]The address to remove from blacklist
Returns
string: A message describing the result of the action
"Address removed from blacklist successfully"or"Address is not blacklisted"source
Throws
- When the specified address is invalid.
See also
Usage
- Remove the address from the blacklist
-- find an advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local address = { 16, 25, 4, 21, 6, 19, 33, 22 } interface.removeFromBlacklist(address)
removeFromWhitelist
(address)
source Advanced Crystal Interface
Removes the specified address from the whitelist.
Parameters
address:number[]The address to remove from whitelist
Returns
string: A message describing the result of the action
"Address removed from whitelist successfully"or"Address is not whitelisted"source
Throws
- When the specified address is invalid.
See also
Usage
- Remove the address from the whitelist
-- find an advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local address = { 26, 6, 14, 31, 11, 29 } interface.removeFromWhitelist(address)
restrictNetwork
(enable)
source Advanced Crystal Interface
Sets the Stargate to enable or disable declining connections from foreign networks.
When the network restriction is enabled, only Stargates with matching Stargate network will be able to establish a connection to this Stargate. Outgoing connections are not affected.
9-chevron address connections bypasses the network restrictions.
Parameters
enable:booleanWhether the network restriction should be enabled.
See also
Usage
- Enable network restriction
-- find an advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: interface.restrictNetwork(true)
setFilterType
(type)
source Advanced Crystal Interface
Sets the filter type for the Stargate.
Only one filter type can be active, either whitelist, or blacklist (or none to disable the filter).
Parameters
type:numberThe identifier of the filter type0 None
1 Whitelist
-1 Blacklist
Returns
number: the filter type identifier that was set
See also
Usage
- Set the filter type to blacklist
-- find an advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local FilterType = { None = 0, Whitelist = 1, Blacklist = -1 } interface.setFilterType(FilterType.Blacklist)
setNetwork
(network)
source Advanced Crystal Interface
Sets the network identifier for the Stargate.
Parameters
network:numberThe identifier of the Stargate network (any number)
See also
Usage
- Set the network of the Stargate
-- find an advanced crystal interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local network = 415252 -- could be any number interface.setNetwork(network)
Iris control
Iris related methods are available even when the Stargate does not have an iris installed. However, they are not available for the Tollan Stargate which can’t have an iris.
getIris
()
source Retrieves the identifier of the currently installed iris on the Stargate.
Returns
string: The identifier of the iris (e.g.sgjourney:naquadah_alloy_iris)
Returnsnilif there is no iris installed
See also
closeIris()openIris()stopIris()getIrisProgress()getIrisProgressPercentage()getIrisDurability()getIrisMaxDurability()
Usage
- Check the installed iris
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local iris = interface.getIris() if iris then print("The Stargate has an iris installed: "..iris) else print("The Stargate does not have an iris installed") end
closeIris
()
source Instruct the Iris to start closing. The function does not wait for the iris to close.
Returns
boolean:falsewhen the iris is already being closed (in motion) by a computer,trueotherwise. Can returntrueeven when there is no iris installed.
See also
getIris()openIris()stopIris()getIrisProgress()getIrisProgressPercentage()getIrisDurability()getIrisMaxDurability()
Usage
- Close the iris
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local closing = interface.closeIris() if closing then print("Closing the iris...") else print("The iris is already being closed by a computer...") end
openIris
()
source Instruct the Iris to start opening. The function does not wait for the iris to open.
Returns
boolean:falsewhen the iris is already being opened (in motion) by a computer,trueotherwise. Can returntrueeven when there is no iris installed.
See also
getIris()closeIris()stopIris()getIrisProgress()getIrisProgressPercentage()getIrisDurability()getIrisMaxDurability()
Usage
- Open the iris
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local opening = interface.openIris() if opening then print("Opening the iris...") else print("The iris is already being opened by a computer...") end
stopIris
()
source Instruct the Iris to stop. The function does not wait for the iris to stop.
Returns
boolean:falsewhen the iris is already being stopped by a computer,trueotherwise. Can returntrueeven when there is no iris installed.
See also
getIris()closeIris()openIris()getIrisProgress()getIrisProgressPercentage()getIrisDurability()getIrisMaxDurability()
Usage
- Stop the iris
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local stopped = interface.stopIris() if stopped then print("Stopped the iris...") else print("The iris is already being stopped by a computer...") end
getIrisProgress
()
source Retrieves the internal iris closing progress.
This progress is internally used for blocking the gate by the iris.
Returns
number: The internal iris closing progress
0when the iris is fully opened or not installed on the gate
58when the iris is fully closed.
See also
getIrisProgressPercentage()getIris()closeIris()openIris()stopIris()getIrisDurability()getIrisMaxDurability()
getIrisProgressPercentage
()
source Retrieves the percentage of the iris closing progress.
Returns
number: The percentage (decimal) of the iris closing progress
0when the iris is fully opened or not installed on the gate
100when the iris is fully closed
See also
getIris()closeIris()openIris()stopIris()getIrisProgress()getIrisDurability()getIrisMaxDurability()
Usage
- Get the iris closing percentage
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local progress = interface.getIrisProgressPercentage() if progress == 0 then print("Iris is open") elif progress == 100 then print("The iris is fully closed") else print("The iris is "..math.floor(progress).."% closed") end
getIrisDurability
()
source Retrieves the iris remaining durability.
Returns
number: The remaining durability of the iris
See also
getIrisMaxDurability()getIris()closeIris()openIris()stopIris()getIrisProgress()getIrisProgressPercentage()
Usage
- Get the iris durability
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local durability = interface.getIrisDurability() local maxDurability = interface.getIrisMaxDurability() print("The iris durability: "..durability.."/"..maxDurability.." "..math.floor(durability/maxDurability*100).."%")
getIrisMaxDurability
()
source Retrieves the iris maximum durability.
Returns
number: The maximum iris durability
See also
getIris()closeIris()openIris()stopIris()getIrisProgress()getIrisProgressPercentage()getIrisDurability()
Usage
- Get the iris durability
-- find any interface connected to the computer local interface = peripheral.find("advanced_crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("crystal_interface") or peripheral.find("basic_interface") if interface == nil then error("The interface is not connected") end -- use the interface: local durability = interface.getIrisDurability() local maxDurability = interface.getIrisMaxDurability() print("The iris durability: "..durability.."/"..maxDurability.." "..math.floor(durability/maxDurability*100).."%")